The security of its IoT devices is the greatest commitment of Libelium. As IBM X-Force announced last week that there were some vulnerabilities in the Meshlium IoT Gateway, new actions were taken immediately by our R&D team offering a new software version released on August 1st.
The Libelium sensor platform was initially created as an open source developing platform ready to be used by researchers and developers to have total control on the sensor nodes and the IoT Gateways. That is how six years ago the Libelium sensor platform became a worldwide IoT market solution.
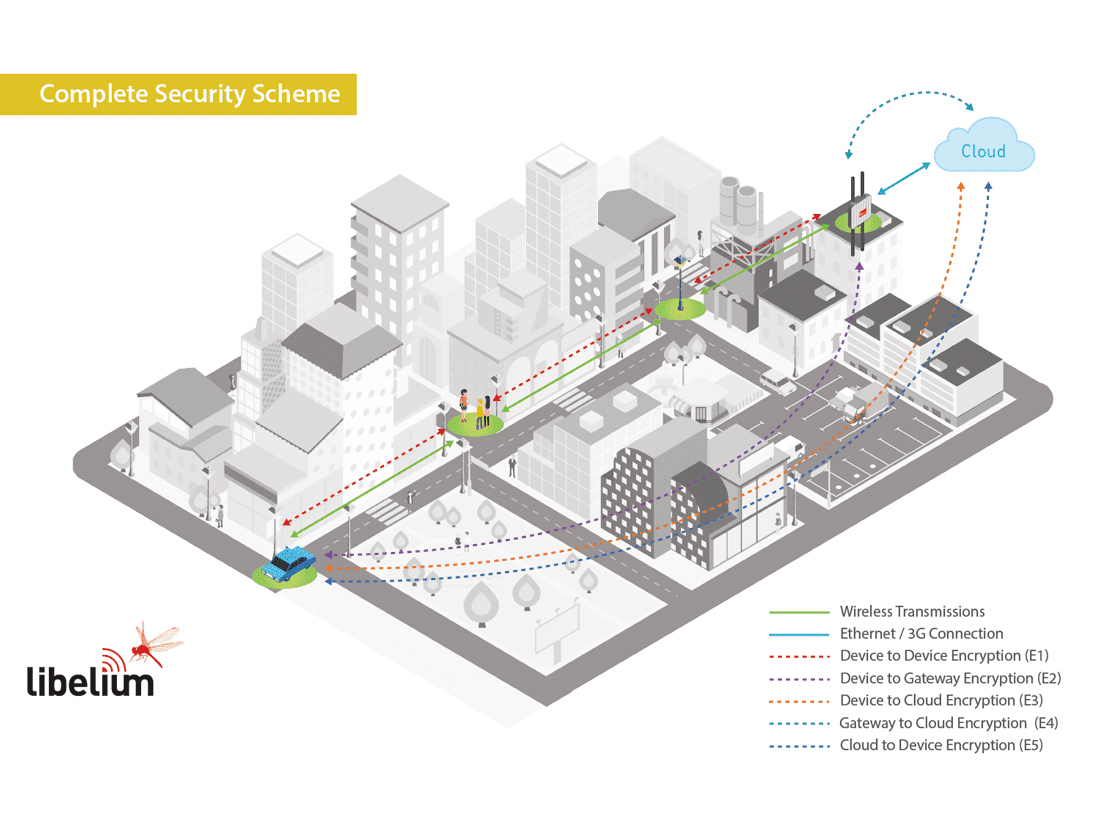
From the outset, we focused on giving to the developers the right tools (API + SDK) so that they could have total control in any respect of the configuration and performance. Regarding the security of the data gathered and transmitted our devices offer the possibility to create up to 5 levels of encryption as it is published in the article titled IoT Security Infographic – Privacy, Authenticity, Confidentiality and Integrity of the Sensor Data. “The Invisible Asset”. These levels are composed by symmetric encryption techniques using the encryption technique AES 256 on the link, network and application layers, and the RSA 1024 on the application layer.
When these encryption techniques are properly set by developers they may achieve the four main security features for its IoT projects: Privacy to ensure that only the desired sensor devices and gateways are part of the network; Authenticity to warrant that the supposed sender is the real sender; Confidentiality to guarantee that the data is only readable by the proposed destination; and Integrity to make sure that the information contained in the original message remains intact.
To ensure all these features nodes must be properly configured, however it seems IBM did not applied the right configuration for their demo at the Black Hat 2018 Conference. In these tests the researchers did not apply the symmetric encryption between the node and the Cloud platform using the AES 256 technique. This encryption, along with a signed and seeded packet (RSA 1024), ensures that the information could not be corrupted or changed as the attackers cannot open the packet and access to the info, because the keys are stored on each node and the Cloud server, not in the Meshlium IoT Gateway. In this sense, potential hackers could not even perform a “man in the middle” attack as the packets are signed and have several internal counters to ensure no retransmissions from invalid sources that were performed.
Using in that demo a basic sensor node configuration scheme instead of applying the complete encryption layers, provided by Libelium, shows a not trustworthy environment, far away from real case developments. This situation may lead to think that this simple configuration scheme was created to easily make some assumptions about security leaks on the information of the sensor nodes when they simply do not exist when the right configuration is performed.
In conclusion, when the security options are properly set, even if the network transmission or the IoT Gateway are compromised, the data will still be secured and it will not be possible to corrupt it or change it. The most important thing is not only to have the right tools, but also know how to configure and use them properly.
For more info about the Libelium platform security features go to:
https://www.libelium.com/iot-security-infographic-privacy-authenticity-confidentiality-and-integrity-of-the-sensor-data-the-invisible-asset/
To know more about the Encryption Libraries implemented by Libelium go to:
https://www.libelium.com/products/waspmote/encryption
Or just contact our team:
https://www.libelium.com/contact/