Home / Casos de Éxito / Detección de niveles de radiación en Fukushima
 Inmediatamente después del terremoto, el tsunami inutilizó el suministro eléctrico y los sistemas de refrigeración de tres de los reactores de Fukushima Daiichi, provocando un accidente nuclear. Los tres núcleos se fundieron en gran parte en los tres primeros días, lo que calificó el accidente de 7 en la escala INES, debido a las elevadas emisiones radiactivas de los primeros días. Afortunadamente, no se han producido muertes ni casos de enfermedad por radiación a causa del accidente nuclear, pero más de 100.000 personas tuvieron que ser evacuadas de sus hogares para garantizarlo.
Respuesta de Libelium
El desastre de Fukushima también conmocionó a España, y los ingenieros de Libelium empezaron a pensar en desarrollar una nueva placa de sensores para medir la radiación. Antes de marzo de 2011, era muy difícil encontrar medidores de radiación en el mercado, y casi imposible encontrar uno asequible para la mayoría de los ciudadanos. Basándose en este problema, Libelium decidió desarrollar un escudo sensor de radiación para la plataforma Arduino debido a su asequibilidad y aparente ubicuidad.
En menos de un mes, probamos y verificamos una serie de tubos Geiger de distintos fabricantes, y después diseñamos la placa para conectar el tubo y mostrar la radiación en una pantalla LCD. Como resultado, se enviaron gratuitamente una serie de placas al Tokyo Hackerspace y a otros grupos de trabajo de Japón.
El principal objetivo de la placa de sensores de radiación para Arduino era ayudar a los japoneses a medir los niveles de radiación en su vida cotidiana tras el desastre de Fukushima. Libelium quería dar a los ciudadanos la oportunidad de controlar estos niveles por sí mismos en lugar de depender de las autoridades locales. El diseño de la placa era de hardware abierto y el código fuente se publicó bajo licencia pública general (GPL).
Además de la Placa de Sensores de Radiación para Arduino, Libelium lanzó un par de meses más tarde la Placa de Sensores de Radiación para Arduino. Placa de sensor de radiación para Waspmote. La idea es simple, cada nodo actúa como un sistema autónomo e inalámbrico. Contador Geiger. Mide el número de recuentos por minuto detectados por el tubo Geiger y envía este valor mediante los protocolos ZigBee y GPRS al punto de control. El sistema se alimenta con baterías internas de alta carga que garantizan una vida útil de años.
Inmediatamente después del terremoto, el tsunami inutilizó el suministro eléctrico y los sistemas de refrigeración de tres de los reactores de Fukushima Daiichi, provocando un accidente nuclear. Los tres núcleos se fundieron en gran parte en los tres primeros días, lo que calificó el accidente de 7 en la escala INES, debido a las elevadas emisiones radiactivas de los primeros días. Afortunadamente, no se han producido muertes ni casos de enfermedad por radiación a causa del accidente nuclear, pero más de 100.000 personas tuvieron que ser evacuadas de sus hogares para garantizarlo.
Respuesta de Libelium
El desastre de Fukushima también conmocionó a España, y los ingenieros de Libelium empezaron a pensar en desarrollar una nueva placa de sensores para medir la radiación. Antes de marzo de 2011, era muy difícil encontrar medidores de radiación en el mercado, y casi imposible encontrar uno asequible para la mayoría de los ciudadanos. Basándose en este problema, Libelium decidió desarrollar un escudo sensor de radiación para la plataforma Arduino debido a su asequibilidad y aparente ubicuidad.
En menos de un mes, probamos y verificamos una serie de tubos Geiger de distintos fabricantes, y después diseñamos la placa para conectar el tubo y mostrar la radiación en una pantalla LCD. Como resultado, se enviaron gratuitamente una serie de placas al Tokyo Hackerspace y a otros grupos de trabajo de Japón.
El principal objetivo de la placa de sensores de radiación para Arduino era ayudar a los japoneses a medir los niveles de radiación en su vida cotidiana tras el desastre de Fukushima. Libelium quería dar a los ciudadanos la oportunidad de controlar estos niveles por sí mismos en lugar de depender de las autoridades locales. El diseño de la placa era de hardware abierto y el código fuente se publicó bajo licencia pública general (GPL).
Además de la Placa de Sensores de Radiación para Arduino, Libelium lanzó un par de meses más tarde la Placa de Sensores de Radiación para Arduino. Placa de sensor de radiación para Waspmote. La idea es simple, cada nodo actúa como un sistema autónomo e inalámbrico. Contador Geiger. Mide el número de recuentos por minuto detectados por el tubo Geiger y envía este valor mediante los protocolos ZigBee y GPRS al punto de control. El sistema se alimenta con baterías internas de alta carga que garantizan una vida útil de años.
Fig. 2.- Placa Waspmote y Sensor de Radiación
Con esta tecnología se pueden conocer las medidas de radiación en tiempo real sin comprometer la vida de los miembros de los cuerpos de seguridad, ya que no tienen que estar dentro del perímetro de seguridad para activar los contadores Geiger. La información se extrae automáticamente y se envía de forma inalámbrica al Gateway de la red. Waspmote tiene un comportamiento cíclico. Duerme la mayor parte del tiempo para ahorrar batería. A intervalos específicos se despierta y durante 1 minuto lee los impulsos que se están generando en el Tubo Geiger calculando los recuentos por minuto. Después compara este valor con los umbrales de alarma ya predefinidos. Si se encuentran valores normales se envían utilizando la radio ZigBee a Meshliumde la red y los valores almacenados en un Internet base de datos.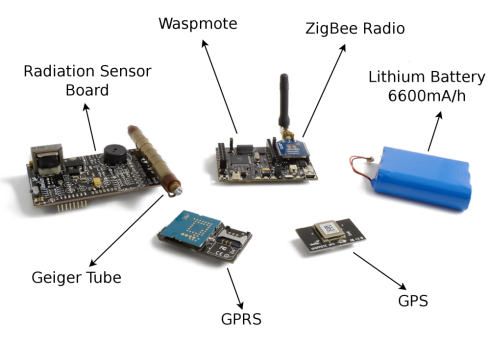
Fig. 3.- Diferentes partes del sistema de medida de Radiación mediante Waspmote
Si los valores superan el umbral de seguridad definido, además de enviarse a través de la red ZigBee se transmiten directamente al cuerpo de seguridad mediante una alarma SMScon el GPRS radio o evento enviado directamente a Internet a través de un socket TCP/IP. Junto con el valor extraído del contador Geiger, Waspmote añade también el GPS información (latitud, longitud) para dar el localización exacta de la fuente de radiación. Además, Libelium ha lanzado recientemente el ¡Waspmote Plug&Sense! Control de Radiación. Esta nueva línea encapsulada permite medir la radiación como se ha explicado anteriormente, pero aumentando las posibilidades gracias a un gran encapsulado.
Fig. 4.- Waspmote Plug&Sense Control de Radiación
Intercambio masivo de datos Antes, los gobiernos eran la única fuente de información sobre los niveles de radiación en torno a una central nuclear o una zona concreta de un país. Pero gracias a una combinación puntera de sensores de radiación baratos (como el Radiation Sensor Board de Libelium), crowdfunding y crowd data sharing, han surgido algunas organizaciones que comparten este tipo de información con todo el mundo. Un ejemplo perfecto es Safecast, una red mundial de sensores para recopilar y compartir mediciones de radiación fundada por un pequeño grupo de personas en EE.UU. y Japón un par de días después del desastre de Fukushima. Consiguieron dinero en una web de crowdfunding y encontraron algunos aliados sobre el terreno en la Universidad Keio de Japón. En sólo cuatro días, el proyecto fue financiado por donantes anónimos y empezó a desplegar sensores en Japón y a mostrar los datos en un sitio web. Los fundadores de Safecast propusieron equipar al mayor número posible de personas en Japón con sensores de radiación de bajo coste. Los voluntarios enviarían sus resultados a través de Internet, que luego se mostrarían como puntos de datos en un mapa de Google. Todo el proyecto sería de código abierto y todos los datos se pondrían a disposición de quien quisiera utilizarlos. Gracias a esta iniciativa, cualquiera puede contribuir a recopilar datos relacionados con una amplia gama de peligros para la salud pública en los que los gobiernos y la industria han mantenido hasta ahora un cuasi monopolio a la hora de medir los peligros para la salud pública. La puesta en común de datos, el crowdsourcing, el crowdfunding y los distintos enfoques de esta metodología están empezando a crear un nuevo escenario en el que todos podemos crear un mundo mejor y más seguro. Si le interesa Waspmoteestaremos encantados de ayudarle a diseñar su sistema. Puede solicitar una oferta de Waspmote aquí. ¡Descubra nuestros kits IoT en The IoT Marketplace!El IoT Marketplace
Comprar kits kits IoT