Home / Success Stories / Libelium Sensors Launch into Space in the First Open Source Satellite
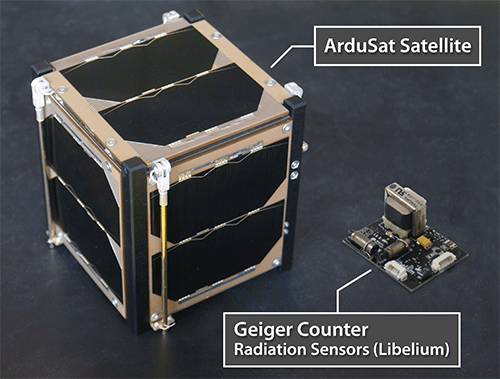
 Once the ArduSat is released into orbit from the HTV-4 cargo (image above) at an altitude of more than 300km, students from a dozen schools across the United States and select schools in Brazil, Guatemala, India, Indonesia and Israel will access and control the satellites for their science experiments, beginning this fall. One of six pre-built experiments uses the Libelium Geiger counter to detect high-energy radiation levels from space.
“Our Radiation Sensors were developed originally to measure radioactivity levels on Earth. We adapted them to meet the satellite’s restrictions in terms of weight, size and power control, in a nice collaboration between Libelium and ArduSat engineering teams,” said David Gascón, co-founder and CTO of Libelium.
Once the ArduSat is released into orbit from the HTV-4 cargo (image above) at an altitude of more than 300km, students from a dozen schools across the United States and select schools in Brazil, Guatemala, India, Indonesia and Israel will access and control the satellites for their science experiments, beginning this fall. One of six pre-built experiments uses the Libelium Geiger counter to detect high-energy radiation levels from space.
“Our Radiation Sensors were developed originally to measure radioactivity levels on Earth. We adapted them to meet the satellite’s restrictions in terms of weight, size and power control, in a nice collaboration between Libelium and ArduSat engineering teams,” said David Gascón, co-founder and CTO of Libelium.
 “We’re making space exploration affordable and accessible to everyone, with a space platform that lets the users innovate. The spirit of discovery and sharing that inspires open source development fits perfectly with this aim and makes it come to life,” said Peter Platzer, CEO of NanoSatisfi, ArduSat’s parent company.
ArduSat Pre-built Experiments include:
“We’re making space exploration affordable and accessible to everyone, with a space platform that lets the users innovate. The spirit of discovery and sharing that inspires open source development fits perfectly with this aim and makes it come to life,” said Peter Platzer, CEO of NanoSatisfi, ArduSat’s parent company.
ArduSat Pre-built Experiments include:
Stay up to date in IoT!
Sign up to our newsletter and receive the latest, exciting news.
More than 18 years of experience in IoT support us.


















© Libelium Comunicaciones Distribuidas S.L. | Terms And Conditions | Privacy Policy | Cookies Policy | Security Policy | Reporting Channel