Home / Success Stories / Urban Resilience in the Smart City: River Flood and Forest Fire Early Detection
Cities adapt for resilience
Pioneered by the Rockefeller Foundation, the 100 Resilient Cities (100RC) organization supports a view of resilience that includes not just the shocks—earthquakes, fires, floods—but also the stresses that weaken the fabric of a city on a day-to-day basis. By addressing both factors, a city can improve its response to adverse events, and is overall better able to deliver basic functions in good times and bad, to all populations.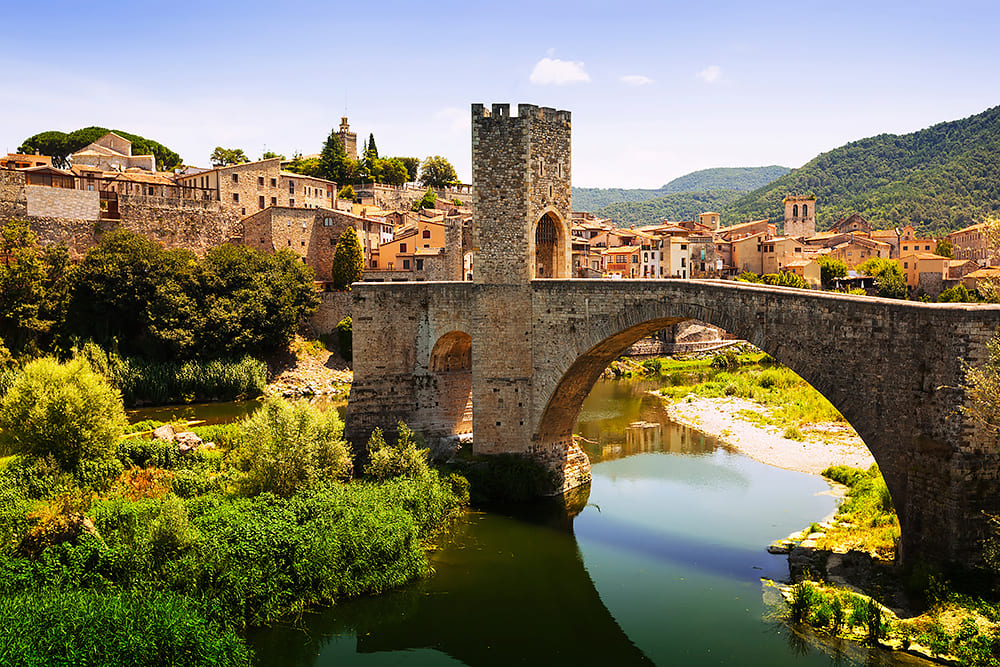
Cities in La Garrotxa span a region comprising protected lands, urban areas and industry
Urban resilience through city management
This key idea motivated Opticits, a Barcelona startup from the IQS-University of Ramon Llull, to work with Sigma, a public municipal organization in charge of environment and services, to create and deploy a City Resilience Management platform that integrates Libelium’s Waspmote Plug & Sense! sensor nodes and Meshlium gateways. Opticits’ experience in the industrial and petrochemical sectors led it to develop an IT and management solution that makes cities urban resilient, more efficient and sustainable. Based on collaboration among local authorities, the system guides urban planning decision makers and city managers. Early Smart City pilots and proof-of-concept projects have evolved to larger scale installations designed to stay in place for decades. In Spain, Opticits’ initial urban resilience assessment project in Barcelona (1.621.000 inhabitants and 102 km2) was reproduced at laboratory scale in Tremp (6.200 inhabitants and 310 km2), then subsequently deployed on a wider scale with a regional focus in La Garrotxa (54.000 inhabitants and 534 km2). La Garrotxa serves as a test bed for managing resilience in a community of 21 municipalities, with a model that other urban areas may readily incorporate. La Garroxta is a region in the Girona province of Catalonia, located between the Pyrenees Mountains and the Mediterranean Costa Brava. Well known for its volcanic natural park, the region of over 50,000 inhabitants has an industrial tradition and an agricultural one, and is noted today for its meat industry. This mixed urban-industrial economic profile is representative of many areas of Europe, and the population enjoys a per capita income well within the EU average.
The region of La Garrotxa, located between the Pyrenees and the Costa Brava
With Opticits’ HAZUR software platform, those charged with managing resilience are instantly alerted to potential cascading effects, and are provided with the detail and information they need to adequately respond. The system helps manage the complexity of the situation and develop strategic planning choices. HAZUR includes an assessment module to determine which sensors to deploy. Information from the Waspmote nodes feeds into a city management dashboard to monitor levels of the river, CO2, fire sensors, among the 40 different types of sensors deployed.Sensor deployment: Large, open, flexible
In La Garrotxa, 35 Waspmote sensor nodes power three main application configurations, measuring parameters for forest fire prevention, river flood monitoring, and ambient control, such as air quality and greenhouse gases. In each configuration the Waspmote Plug & Sense! nodes are equipped with solar panels and rechargeable batteries, to ensure years of autonomy. The Waspmotes themselves are IP65 rated and designed to be highly modular to allow a sensor to be removed or added in seconds. In La Garrotxa, the devices communicate via Wi-Fi and are able to reach upwards of 40 km in Line of Sight (LOS) conditions using the 868MHz module.Forest Fire Prevention (11 nodes)
In this configuration Waspmote Plug & Sense! Smart Environment monitors four different parameters to detect and prevent forest fires, with sensor probes in trees and on rooftops measuring: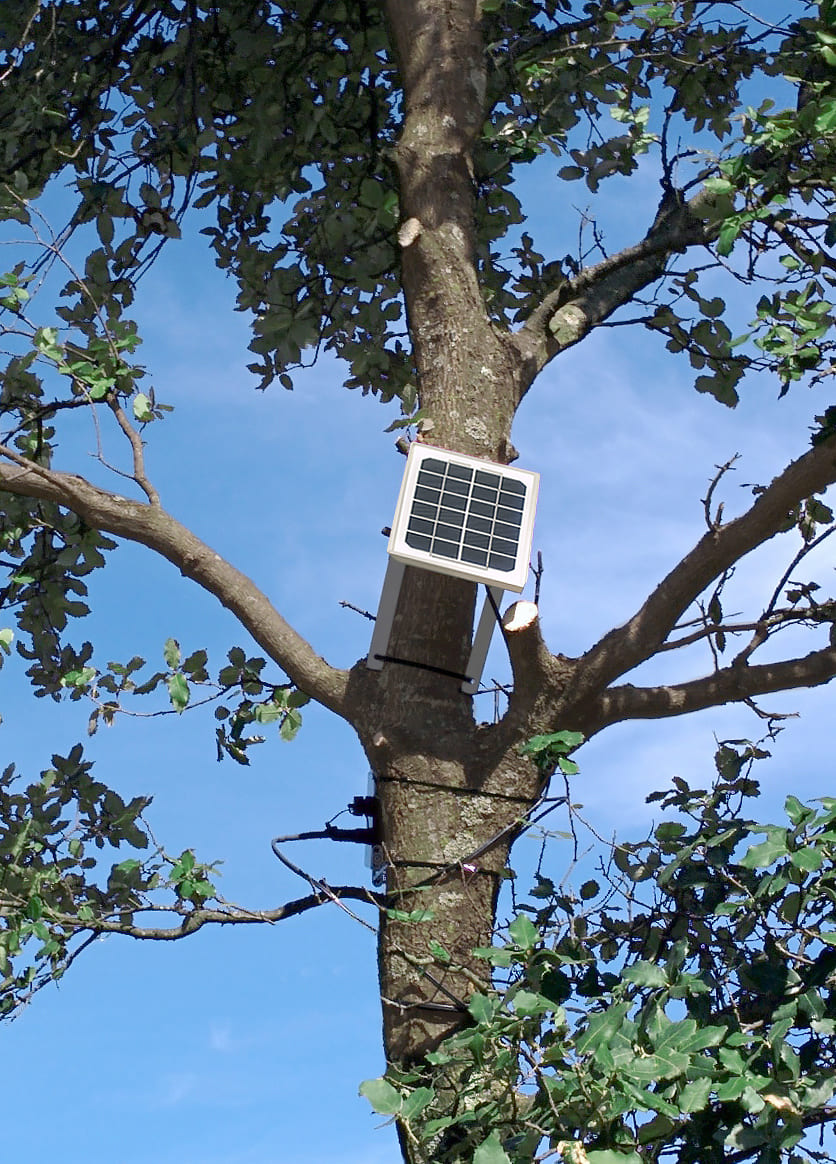
Waspmote Plug & Sense! Smart Environment sensor node
River Monitoring / Flood Prevention (16 nodes)
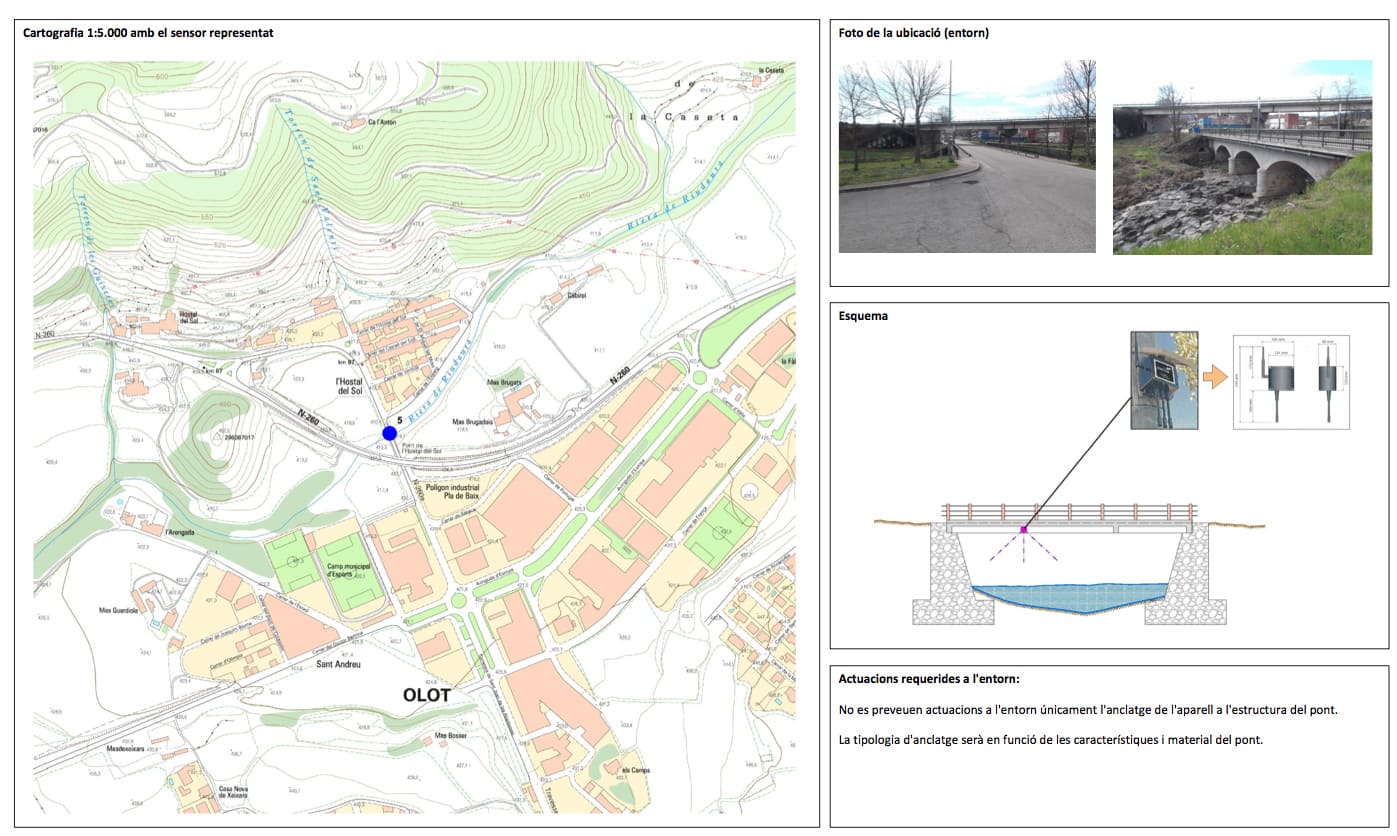
Detail of river monitoring sensor node placement in Olot, La Garrotxa
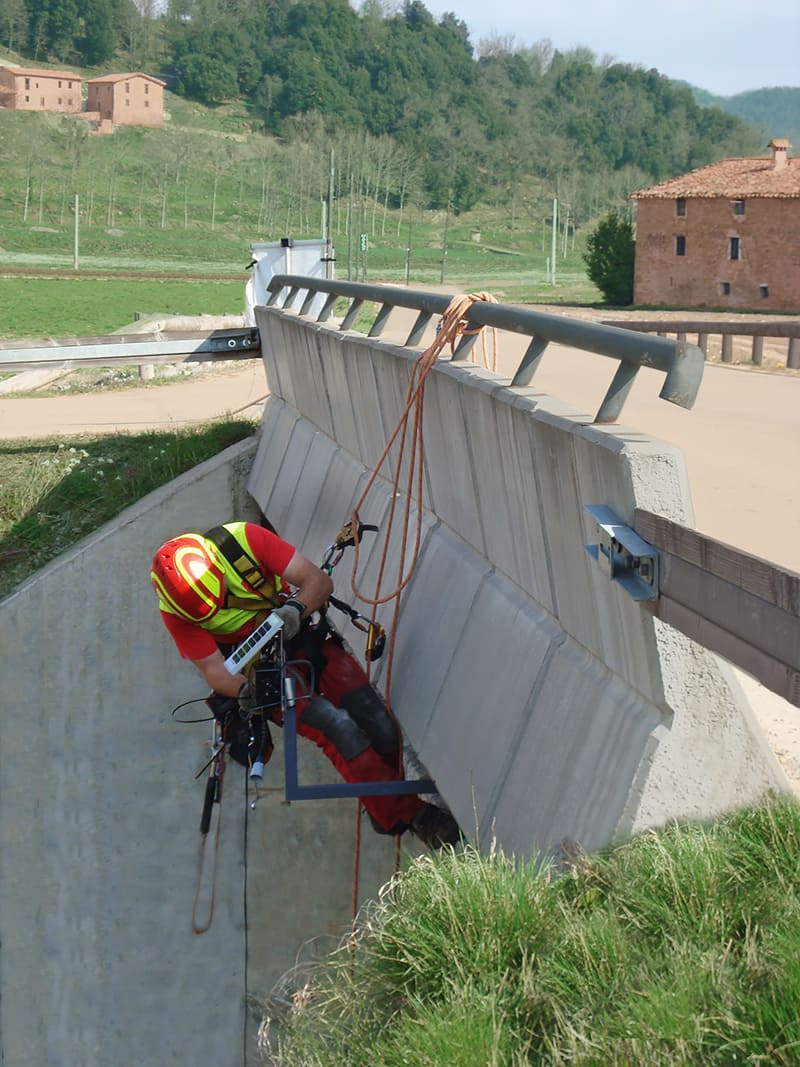

Antenna and sensor node placement to detect water level for flood prevention
Ambient Control (7 nodes):
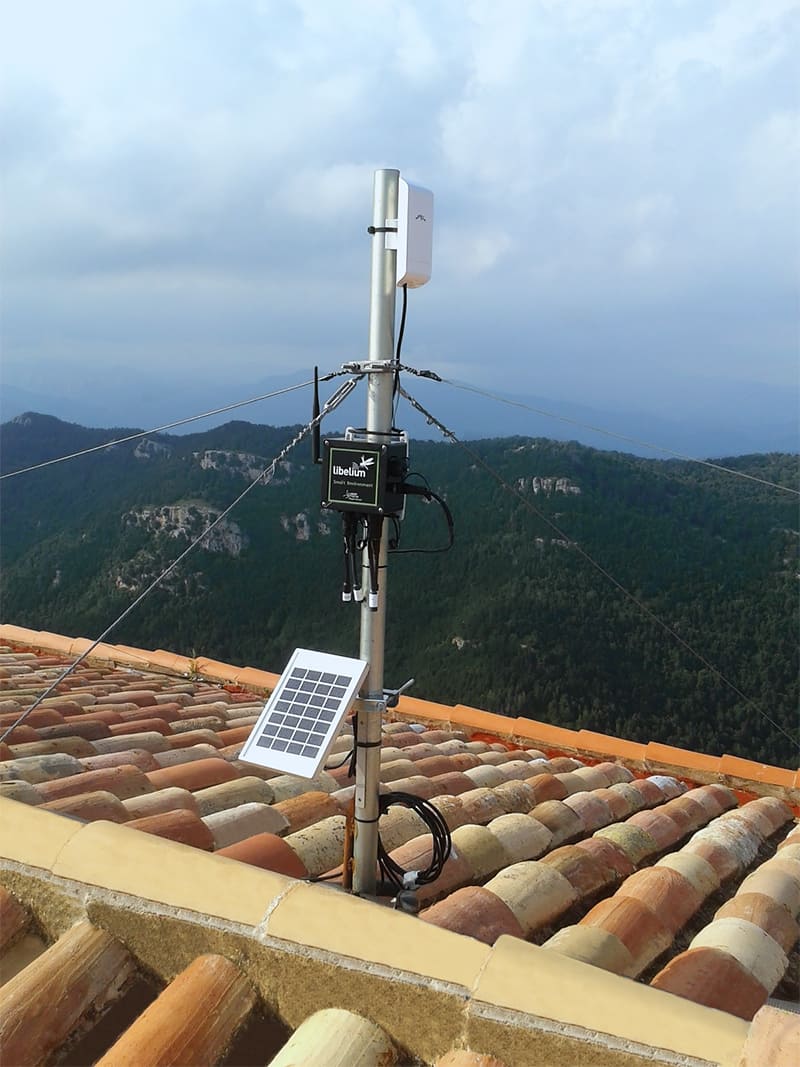

Smart Environment sensor node can harvest energy and receive new calibrated probes
Also deployed in the wireless sensor network are eight Meshlium gateways in place outdoors throughout the area to ensure long-range transmission of data to the Cloud, and several external Wi-Fi antennas to boost Wi-Fi coverage. Meshlium is a Linux router that works as a multiprotocol gateway for the Waspmote wireless sensor networks. Meshlium can contain five different radio interfaces; including Wi-Fi, 3G/GPRS, Bluetooth, ZigBee, and can integrate GPS modules for mobile and vehicular applications.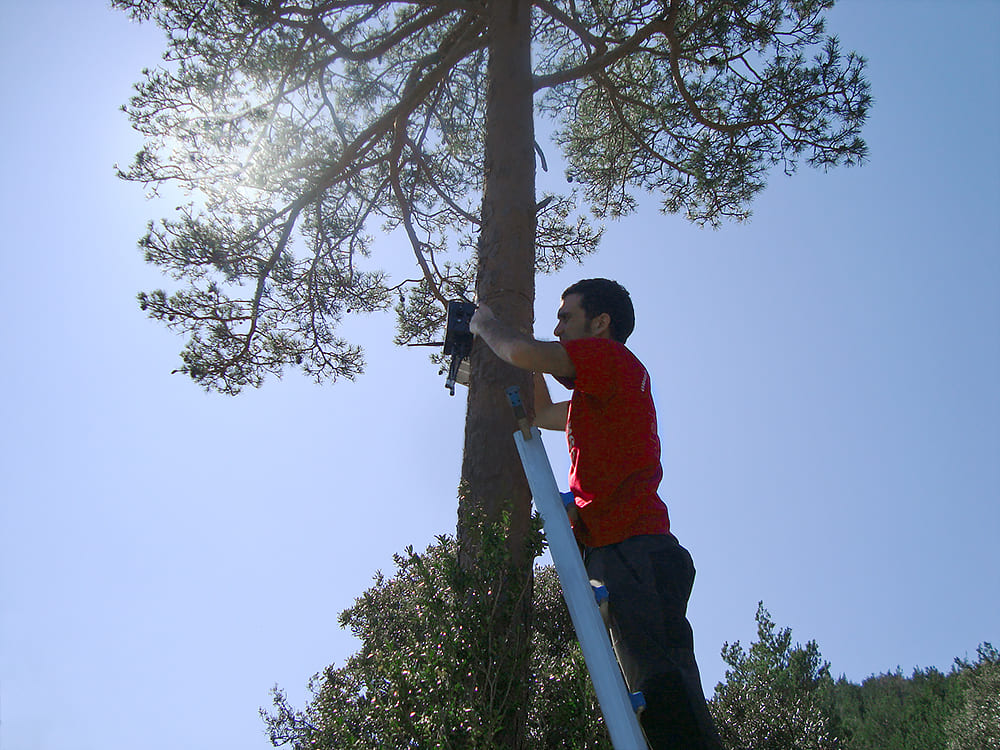
Installing sensor nodes in optimal locations for forest fire detection
WSN Deployment: Location, Location, Location
The territory of La Garrotxa is a mix of town, countryside and rugged forest in an area protected by environmental regulation and historical patrimony laws. Setting up the wireless sensor network included a planning phase to analyze sensor placement, taking into account antennae range, positioning of solar panels in forested areas, and the design and construction of structures to install the river sensors. Once in place Waspmote sensors effectively capture and transmit the information needed to monitor water quality, air pollution, fire hazards, and other threats that the local resilience managers can read in real time. The high performance of Waspmote makes the readings accurate and data transmission is highly reliable. “Libelium’s wireless sensor networks are an integral part of bringing an affordable solution to La Garrotxa,” said Ignasi Fontanals, CEO and co-founder of Opticits. “The great thing we identified with the Sigma team is that the Libelium sensor platform is so easy to deploy and scale. That makes a big difference as cities and regions adapt to unforeseen changes now and in the future.” Opticit’s HAZUR dashboard is the basis of many system tools used to oversee the data capture and integration, and to track and manage key performance indicators (KPI) that support working structures and responsibilities in regional services. The system is managed with a software dashboard, known as a “situation room,” where La Garrotxa resilience managers view an interdependence map that displays the vulnerability and resilience of the infrastructure networks.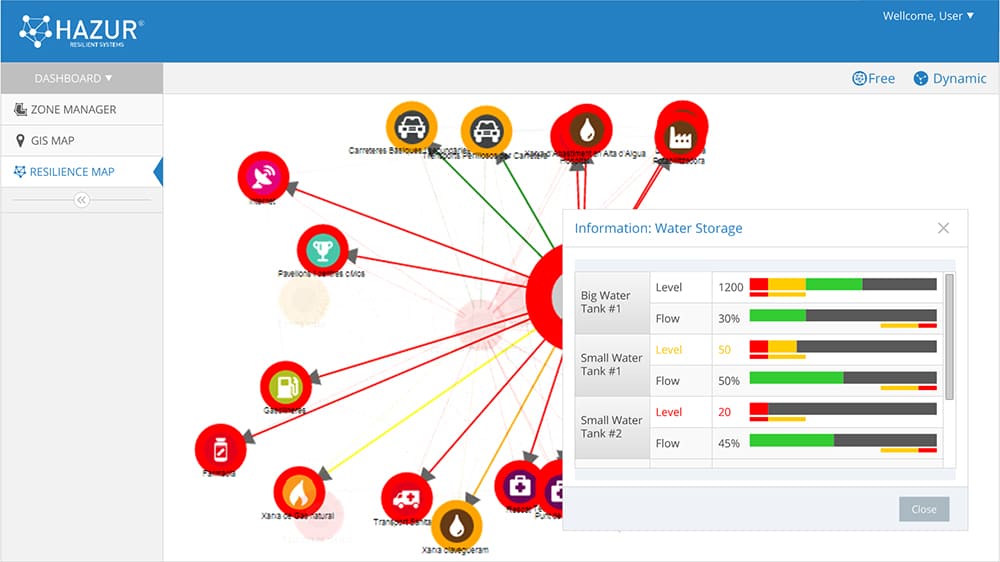
A user’s view of Opticits’ HAZUR situation room software interface
Urban planning is long term
For Francesc Canalias, General Manager at Sigma, the effectiveness of the Opticits system relies on data from Libelium sensor devices. “To bring urban resilience to La Garrotxa, we had a plan for the long term and needed a sensor network platform that was extremely flexible and adaptable, able to meet the dynamic requirements of various urban services that work as an ecosystem. Libelium’s Waspmote sensors and Meshlium gateway were easy to install and integrate with HAZUR, so they are the perfect fit in this regard.” With the implementation of HAZUR and Libelium sensors, the territory of La Garrotxa can readily manage critical facets of its infrastructure and public services. The system installation has already led to greater cooperation between public and private interests within the region, who continue working together to identify threats and remedy areas of non-compliance. “The Internet of Things represents an opportunity for industry and entrepreneurs to invent and innovate, to deploy technology that leads to a better quality of life. Spain is fertile ground for the Internet of Things because necessity, know-how and the means come together to solve problems,” said Alicia Asin, CEO and co-founder of Libelium. Technological innovation may bring its greatest benefits in projects of social utility. In Barcelona and in La Garrotxa, city managers and IT project managers have created a new working dynamic by setting priorities that align communities as they strive to improve resilience for neighborhoods and for an entire region. Spain is developing an ecosystem comprised of technology enterprises, universities, private industry, municipalities, regional government stakeholders working together to benefit cities where we live and work. Read more about our product lines in Waspmote, Plug & Sense! and Meshlium websites. If you are interested in purchase information please contact the Commercial Department. Discover our IoT Kits at The IoT Marketplace!Stay up to date in IoT!
Sign up to our newsletter and receive the latest, exciting news.
More than 18 years of experience in IoT support us.


















© Libelium Comunicaciones Distribuidas S.L. | Terms And Conditions | Privacy Policy | Cookies Policy | Security Policy | Reporting Channel